© Benaki Phytopathological Institute
Kioulos & Koliopoulos
22
field trials in backyard habitats in Australia
where it successfully managed to keep mos-
quito larval habitats free of mosquito eggs,
larvae and pupae up to 5 weeks post-appli-
cation (Webb and Russell, 2012). Because of
its non-biochemical mode of action no re-
sistance is anticipated. In the present study
the effectiveness of Aquatain
TM
as a mos-
quito control agent was tested in rice pad-
dies under the common cultivation prac-
tices followed in Greece. For this purpose,
a field experiment was set up in rice fields
close to Anthile, Prefecture of Phthiotida,
Greece (38
0
49’08.36”N- 22
0
29’51.89”E) in a
difficult for mosquito control period when
rice plants had completed tillering and flow-
ering, from August to September 2012.
Materials and methods
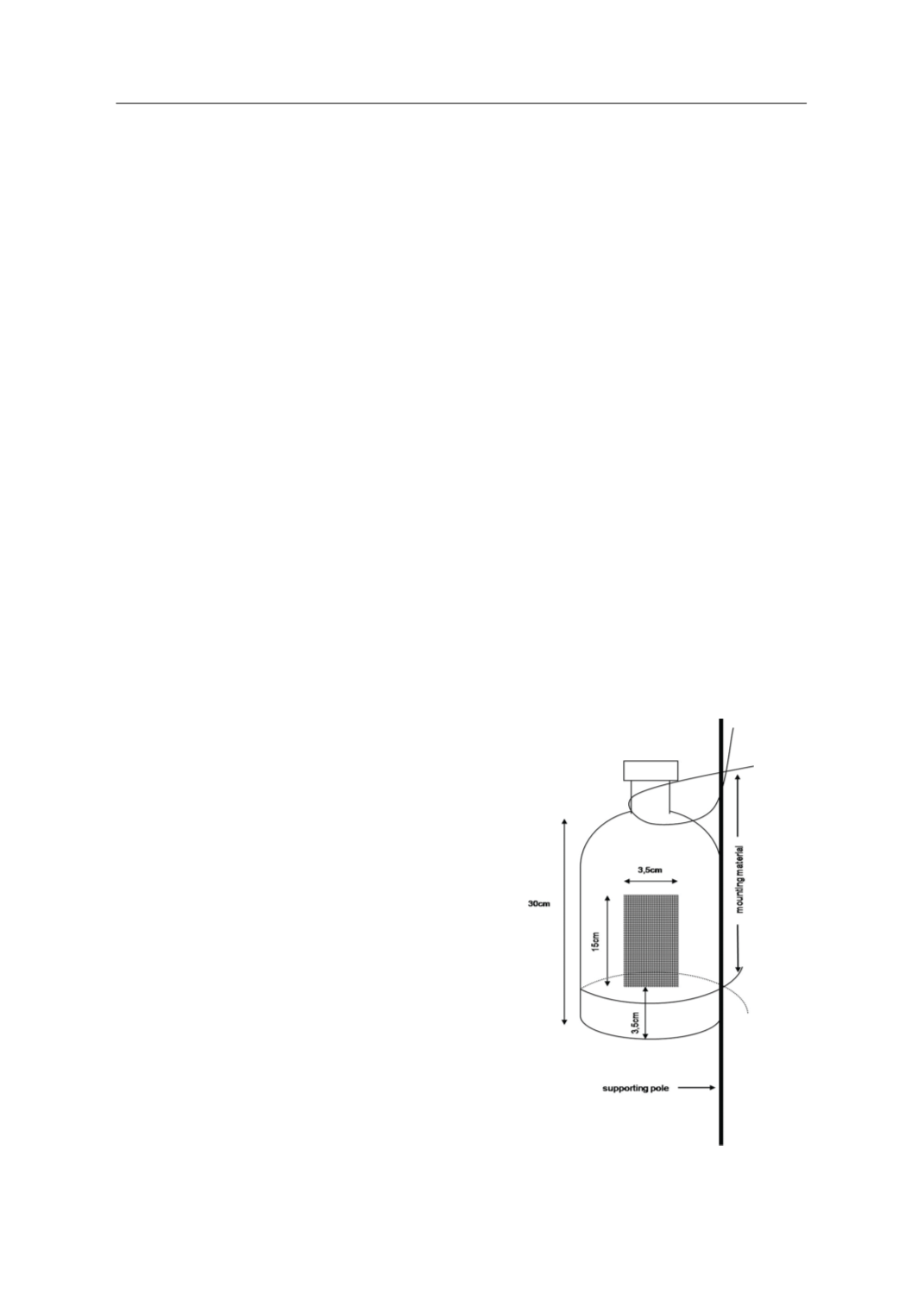
Cylindrical cages were specially construct-
ed by plastic bottles (30cm high, 8cm diam-
eter) with an opening (3.5x15 cm) at 3.5cm
height above the bottom. The opening was
covered with gauze of an appropriate mesh
capable to prevent mosquito larvae from es-
caping but allowing the free movement of
water in the cages (Figure 1). Nine sampling
cages, along three different lines (three cag-
es per line), were selected and marked in
a 1.2 ha (120x100m) experimental paddy
(Figure 2). The first line (line 1) of replicates
was set close to the short edge of the pad-
dy where Aquatain
TM
was applied, the sec-
ond one in the middle of the paddy (line 2)
and the third one at the far distant edge of
the release site (line 3). The sampling cages
were 25m apart in the same line and 30m
apart from the corresponding point in the
adjacent line and from the short edge of the
paddy (Figure 2). An adjacent rice paddy of
the same dimensions which received the
same cultivation and plant protection man-
agement as the experimental paddy but was
not treated with Aquatain
TM
, served as a con-
trol paddy. Sampling cages were set in the
same pattern in the control paddy. An irriga-
tion ditch provided water constantly to both
paddies (experimental and control), where-
as excess water was exiting to the drainage
channel (Figure 2, blue arrows). Plastic cag-
es were tightened on supporting poles and
placed in the rice paddy prior to Aquatain
TM
application. All supporting poles were sub-
merged in such a way that the opening of
the cages was half submerged (10cm from
the base of the cage, Figure 2). Adjustment
of the level of the cages was performed on
the assessment days to match water fluctua-
tion. Twenty fourth-instar larvae (L
4
) of
Culex
pipiens
from a laboratory colony (reared at
Benaki Phytopathological Institute, T=25 ±
2
0
C and 75 ± 5%RH) were placed into each
cage just before Aquatain
TM
application.
Aquatain
TM
was applied into the experi-
mental field by pouring from five different
spots along the short edge (A) of the paddy
(Figure 2) at the labelled rate of 1 ml/m
2
(12L
in total). A single application was performed
on 27
th
August 2012. Efficacy of Aquatain
TM
was assessed by recording larval mortali-
ty 3, 6, 15 and 25 days after application. To
record larval mortality, the contents of the
cages were poured into a white pan in or-
der to count the remained larvae (dead or
alive). After each assessment another batch
Figure 1.
Plastic cage used in the study.


